Combining 8 ISPs with a single mikrotik device
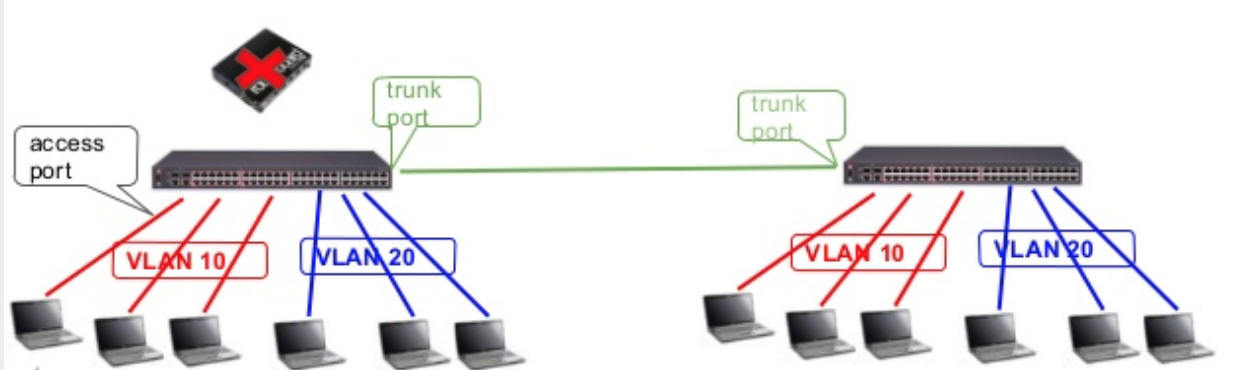
Hello all, this time, we would like to share our project of combining 8 ISPs with a single Mikrotik device. So, our client already subscribes to internet connections from 8 different ISPs, and want to use them to provide internet connections to his customers. The reasons are simple: For availability purposes. If one connection is down, the customer is still able to connect via other links (there are eight connections in total, you know that, right? :-p) To increase capacity and also sharing traffic load among the connections. These mean let say if each link has a 100 Mbps datarate, having 8 of them will result in 800 Mbps in total. Sounds good, right? so this is what we did: configure ONU modems to be in the bridge-mode. The upstream…