Well, we used coaxial ethernet already in our house and it was cool 🙂 can now sharing file, printer, and even do voice communication using netmeeting :-p.(What is ethernet 10baseT, 100baseT, XXbaseYY)
Unfortunately, by the time goes we see that the coaxial network is not reliable as we expect. the biggest issue for coaxial ethernet was the time required to troubleshoot the problem. often happens many times the connectors were not properly installed due to many reasons, computers were kicked, the lid was not tight, computers were accidently shaked and so the LAN card, etc.
This single, simple, and annoying problem cause the WHOLE network broken. we simply cant send data anymore. really not good. so we looking for another technology that accommodates our need. and that is 10baseT.
Actually in order to find out where the problem is quickly, there is a tool named time domain reflector which is able to find out the location where the cable is broken. therefore we can just focus on the area to fix the problem. unfortunately, this tool is quite expensive, and we did not think it was affordable by students like us 😛
So, what is 10baseT?
- 10 means max datarate is 10mbps
- base means it uses baseband signal
- T means we will use twisted pair cable. can be
- UTP – unshielded twisted pair, or
- STP – shielded twisted pair
So, what is XXbaseYY means?
XX means max datarate of the technology
YY means the media. that could be Twisted-pair copper cable, or fiber optic (preferable for high datarate link).
Requirements to build a 10baseT network?
- Ethernet card. some ethernet card support both 10base2 or 10baseT.

- ready to use UTP cable. of course you need a cable as media. in order to make a ready to use UTP cable. you need to crimp the cable. for that you need:
- RJ45 connector.

- UTP cable.

- RJ45 connector.
- HUB. this is the most important part of 10baseT, all physical connections will end up here.

How is it implemented?
10baseT requires a concentrator that centralised all physical links from stations like a star. this is very similar to telecommunication system where all connections from clients goes to central office (CO). the connection then could be extended as network grows. see picture below

How communication happens in the media? and why terminator is needed?
When a station sending, its signal will be received by one port on the hub. this port will then forward the incoming signal to all other ports.
what about the topology?
- Physical. can be star, extended star
- Logical: bus. it uses CSMA/CD for data transfer
pros and cons?
- Pros: more reliable (failure on one cable will not make the whole network broken)
- cons: more cable is needed (all stations should connect to HUB). collisions still happen and communication is half-duplex
Any improvement for the technology?
one very cool improvement in CSMA/CD is the use of switch (instead of hub). switch is a smarter device that analyse the layer2 header (destination MAC address) and forward the frame into specific port. therefore there will be no collision and and full duplex communication can be achieved.
because may people use ethernet, and market is flooded by the products, price is cheaper.
Another important improvement is speed. Ethernet is still developing to reach higher and higher speed. event the speed now can reach 100GBps. see picture below
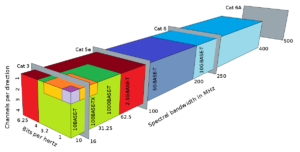
any commercial name for those technologies?
- 10baseT: twisted-pair ethernet
- 100baseT: fast ethernet
- 1000baseT: gigabit ethernet
- 10GbaseT: 10Gbit ethernet
thank you for reading hope you understand “What is ethernet 10baseT, 100baseT, XXbaseYY”