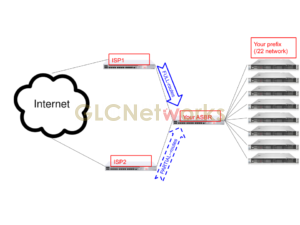
 In the previous articles, we already talk about setting up a BGP session between routers in the form of peering. When a BGP session established, the routers will start to exchange their routing prefix, put them into the main routing table, apply BGP best-path algorithm, and the router will have optimized routes that will be used for FIB (Forwarding Information Base). FULL-routes vs partial-routes on BGP. A question arises, are those routes full or partial? What’s the difference between them? Which one should I pick? Ok here it is:
In the previous articles, we already talk about setting up a BGP session between routers in the form of peering. When a BGP session established, the routers will start to exchange their routing prefix, put them into the main routing table, apply BGP best-path algorithm, and the router will have optimized routes that will be used for FIB (Forwarding Information Base). FULL-routes vs partial-routes on BGP. A question arises, are those routes full or partial? What’s the difference between them? Which one should I pick? Ok here it is:
FULL-routes
a FULL-routes is a whole prefix in the (BGP) world, meaning a collection of all prefix/routes of any AS in the world. in 2018, there are 700 thousand routing entries in FULL-routes, and it keeps growing. It will stop growing until all allocated-prefix been used and announced, or nobody uses it anymore :-p. With FULL-routes, you will get an idea about how the internet looks like, and you can parse them to get an insight into internet connectivity. For example:
- You will know which prefixes belong to which AS
- You will know which AS-path if you want to access a particular IP address.
- Extract prefix from full routes for further processing
- Visualize the data to understand the internet better
well, putting 700 thousand prefixes into a routing table requires resources. a FULL-routes can take up to 400MB RAM and maybe more, and when a packet arrived at a routing table, the router will do a lookup operation on those prefix-entries which consume CPU power. The more its coming, the more CPU power is required.
PARTIAL-routes
As the name suggests, PARTIAL-routes only contains a subset of FULL-routes. take a look of the picture below:
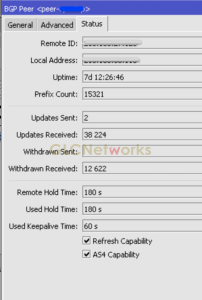
The picture above is an example of a BGP peer that exchanges PARTIAL-routes. As you can see, instead of giving hundreds-of-thousand prefixes, it only exchanges thousands of them. partial-routes usually contain prefixes for different purposes. for example, it can contain a list of:
- Blacklisted prefixes
- Bogon prefixes
- Prefixes of members of an IXP
- etc
How to obtains FULL/PARTIAL routes?
Well, that depends on the provider. Some give full-routes, some only provide partial-routes. At some ISPs, PARTIAL-routes are additional services for their customer.
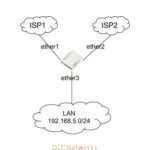
it also depends on the place you do a peering. if you a member of an IXP you will get a PARTIAL-routes that contains prefixes of the member of the IXP.
Which one is better: FULL-routes or PARTIAL-routes?
well, I don’t think this is a mutually-exclusive question because that depends on what you want to achieve. in fact, as you can see picture above, you can combine both into your routing table, and then adjust the BGP-attributes to give the best-path to your customer. FULL-routes vs partial-routes on BGP.
This topic is part of BGP workshop by GLC Networks. for more information, please contact here