When you read this and this articles, there is a term called topology. For those who are not familiar with the term, this article will discuss about the Differences between physical and logical topology?
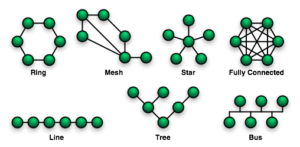
What is physical topology? Physical topology means how the network is shaped physically.
Some examples of physical topology?
- bus
- star, extended star
- ring
- dual ring topology (for redundancy, in case if one ring is broken)
- cellular

What is logical topology? Logical topology means how the data is traveling in the media.
Some example of logical topology?
- token ring. this means there is a token that is always moving around the network from a station to other station. computer can send data only if a token arrive to them.
- Physical implementation
- ring topology. example: FDDI
- star. example: token ring
- Pros and cons:
- pros: there is no collision
- cons: latency, data rate is slow, max 16 mbps
- Physical implementation
- bus. this means, each station can send data anytime, the data is sent to a common media that is shared to other stations (broadcasted). consequently, all other stations can hear the data too, and if there are 2 stations sending data at the same time, a collision happens. CSMA/CD (Carrier Sense Multiple Access / Collision Detection) is the correct term that explains how the bus logical topology works, and the most famous technology that uses the CSMA/CD is ethernet.
- Physical implementation
- bus. example: 10base2 / 10base5
- star or extended star. example: 10baseT
- Pros and cons:
- pros: simple, fast datarate (can be up to 100mbps), cheap
- cons: collisions, there more stations in the network the more worse the performance because collision will happen more often.
- Physical implementation
thank you for reading, hope you understand the “Differences between physical and logical topology”