In this article, we will talk about understanding how switch works or bridge. This is a basic knowledge that network engineer must know. This is so basic where if you failed to understand this you will be having difficulties when doing troubleshooting problem in your network, especially related to this devices.
So, what is (ethernet) switch / bridge?
switch is a layer 2 device that is used as concentrator (central point) to connects other wired devices that is use ethernet technology.
any picture of ethernet switch?
see picture above
how it connects devices? the picture below explains how devices communicate each other through a concentrator (switch).
is switch an economical solution? perhaps if you compare other technology like ethernet via coaxial cable.
is switch an reliable solution? if you compare switched-ethernet with coaxial-ethernet, switch definitely is more reliable. Before switch is invented, computers were connected in a daisy-chain topology. at the end of connection we put a terminator in order to absorb signal. see picture below
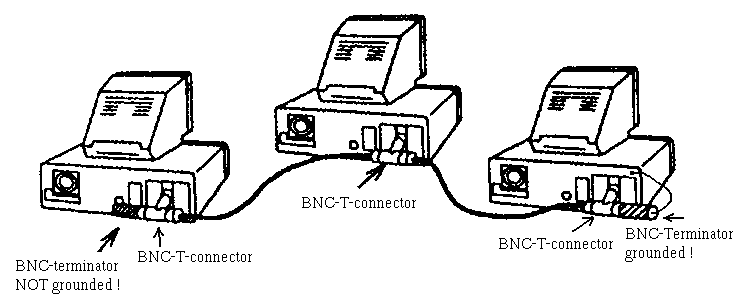
why switched-ethernet is more reliable and better performance? in coaxial-ethernet (10base2), when a problem happens, its hard to find out where the error is. engineer need to check the connector one-by-one, which takes time. another thing is, if one cable is broken, then the whole network will not work. therefore, its very fragile.
coaxial ethernet uses 2 cables (inner and outer) to transmit and receive data to whole network. that means a half-duplex communication, computer cannot receive and send at the same time. and when traffic is high, you can see many collisions happening as 2 stations sending data at the same time, which can lower data rate.
with switched ethernet, if one cable broken, it wont affect other communications. if a port is broken, user can simply plug the cable to other good ports.
In terms of performance, the mechanism inside a switch can enable a full-duplex communication, which could increase performance of whole system as collisions can be avoided.
so how switch works? (Understanding how switch works)
in short, switch works by analysing the layer2 header of incoming frame. each ethernet frame contains 2 addresses: source MAC and destination MAC.
switch learns the source MAC in order to recognise which station connects to which port. this is important to build a MAC forwarding table on switch. this table is a magic secret of how switch can provide duplex communication.
switch then analyse the destination MAC address, lookup the destination MAC address in MAC table, and make forwarding decision to which port it should forward the frame. with this mechanism, other ports cannot hear what other port is sending. and by doing this, full-duplex can be achieved.
please check the animation below to understand the process of MAC learning
i see. what happen, when the destination MAC address is not available in the MAC table, to which port it forwards?
well, in this case, switch will forward the frame to all ports, expecting that a station will reply the message and switch can learn its MAC address to update its MAC lookup table.
ok so thats the end of “Understanding how switch works”